The diet profoundly influences both human health and the environment. Poor dietary habits, particularly those lacking unprocessed, plant-based foods, rank as the leading cause of death globally. They contribute to cardiovascular disease, cancers, and type 2 diabetes. The diet also impacts environmental sustainability, with animal-based foods exerting a far greater toll than plant-based alternatives.
These effects span climate change, land and freshwater use, and biodiversity loss. As plant-based diets gain popularity, they are increasingly recognized for their dual benefits—enhancing health and reducing environmental harm.
Central to this health-environment interplay is the gut microbiome—a dynamic ecosystem of microorganisms residing in the intestines. The diet shapes the microbiome, influencing processes such as digestion, immune function, and overall health. Plant-based diets enrich the gut with short-chain fatty acid (SCFA)-producing bacteria.
These SCFAs maintain gut health by reinforcing the gut barrier, reducing inflammation, and supporting immune balance. Plants also provide polyphenols, compounds that promote beneficial bacteria while suppressing pathogens.
Conversely, diets high in animal-based foods can disrupt gut health. Increased protein fermentation in the gut may lead to systemic inflammation and a weakened gut barrier.
Breakdown products like trimethylamine (TMA), converted in the liver to trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), are linked to cardiovascular diseases and colorectal cancer. These disruptions illustrate the delicate balance the microbiome maintains in response to dietary input, making the choice of foods critical for long-term health.
The interplay between diet and the gut microbiome extends beyond individual health. A healthy microbiome, fostered by diverse plant-based foods, contributes to stronger immunity, efficient energy metabolism, and even mental health. Emerging research has linked gut microbial imbalances to conditions such as depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative diseases, underscoring the far-reaching influence of dietary habits.
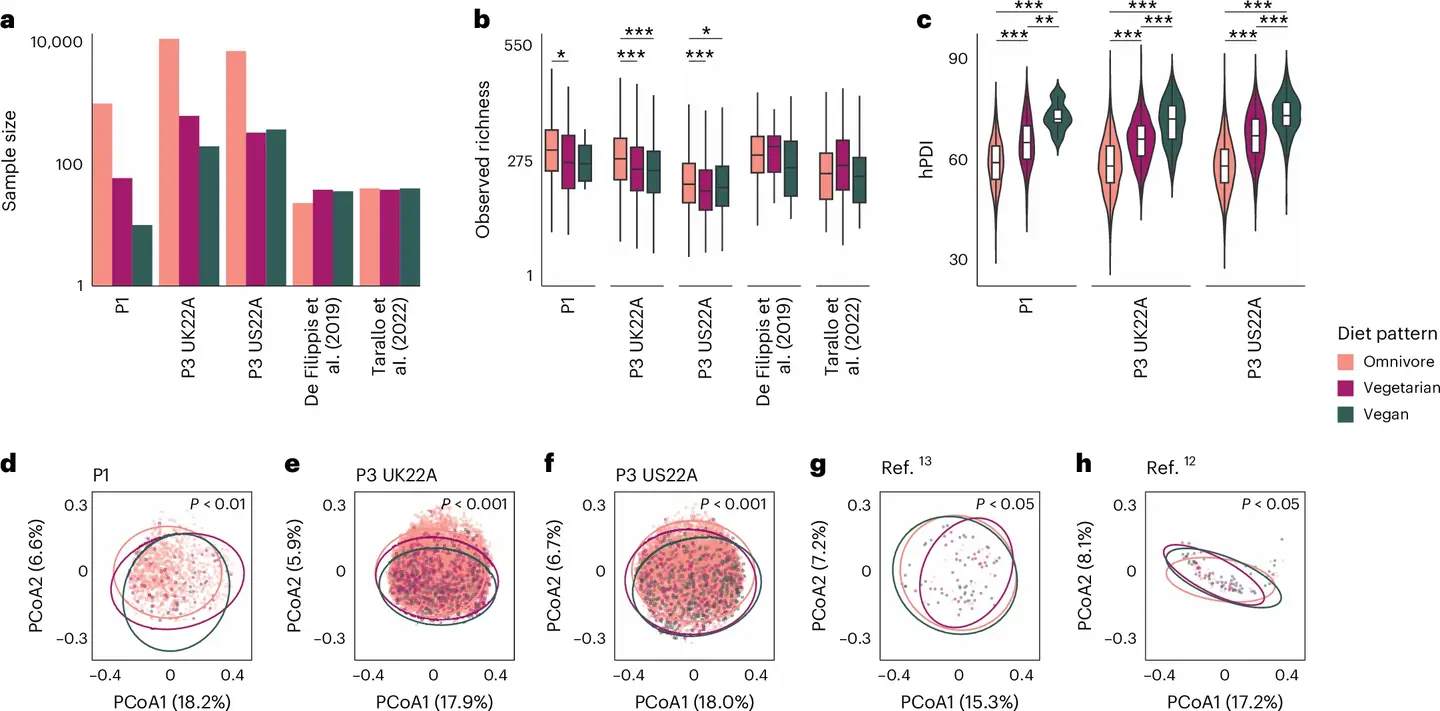
A new study, published in the journal, Nature Microbiology, sheds light on how dietary patterns influence the microbiome. Researchers analyzed data from 21,561 participants across five cohorts in the United States, United Kingdom, and Italy.
Participants were categorized as omnivores, vegetarians, or vegans and provided detailed dietary data through food frequency questionnaires. Stool samples underwent advanced metagenomic sequencing to identify microbial species and their functional roles.
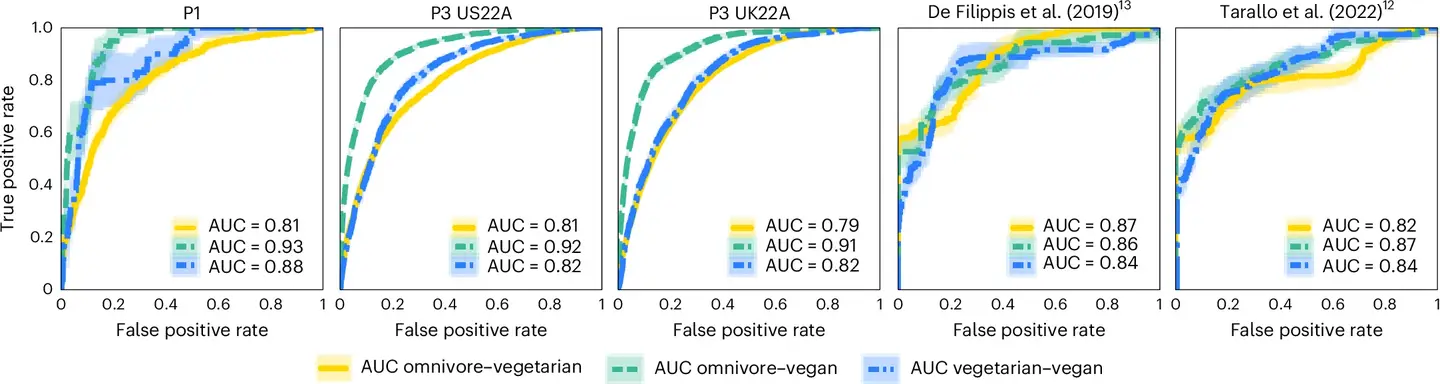
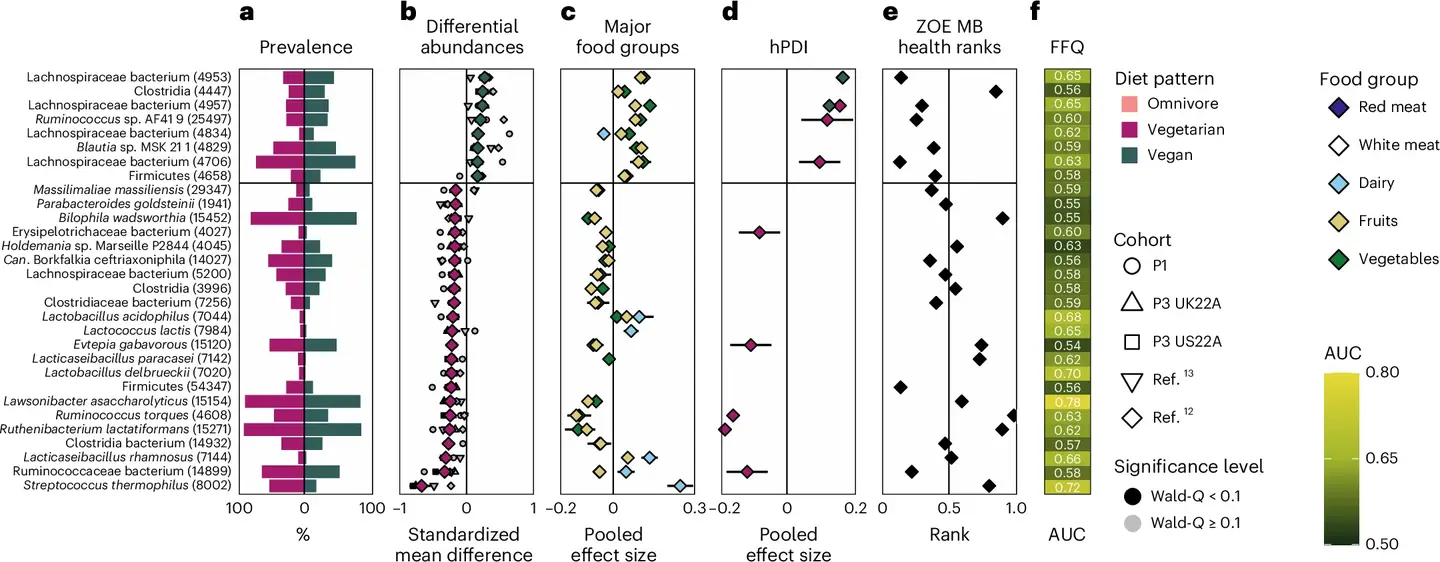
The study’s findings reveal distinct microbial signatures associated with each dietary pattern. Omnivore microbiomes were characterized by microbes linked to meat digestion, such as Ruminococcus torques and Bilophila wadsworthia. These bacteria correlated with inflammation and heightened risks of colon cancer and cardiometabolic diseases.
In contrast, vegan microbiomes showed increased levels of fiber-fermenting bacteria, including species from the Bacteroides and Firmicutes phyla. These microbes produce SCFAs like butyrate, which reduce inflammation and support metabolic and immune health.
Vegetarians displayed microbiomes similar to vegans but included unique microbes like Streptococcus thermophilus, commonly found in dairy products. Notably, while vegetarians and vegans exhibited less bacterial diversity than omnivores, diversity alone is not a definitive measure of microbiome health. The study underscores the importance of bacterial functionality and quality rather than sheer variety.
The study also examined the regional and cultural variations in dietary habits. Participants from Mediterranean regions, for example, consumed diets naturally higher in fresh vegetables, legumes, and olive oil, contributing to favorable microbial profiles. In contrast, diets common in Western countries often featured highly processed foods and red meat, which were associated with less beneficial microbiome compositions.
The research emphasized that dietary quality—not merely dietary pattern—drives microbiome health. Diets rich in plant-based, minimally processed foods foster a favorable microbiome, irrespective of whether one follows a vegan, vegetarian, or omnivorous diet. Reducing intake of highly processed animal products, particularly red meat, was associated with healthier microbial compositions.
An intriguing aspect of the study was the transfer of bacteria from food to the microbiome. Vegans had fewer food-derived bacteria except for those from fruits and vegetables, which were predominant. Conversely, omnivores and vegetarians showed higher levels of bacteria associated with dairy, especially from fermented products. These findings highlight how dietary components directly shape the microbial landscape.
Beyond physical health, the study touched on the psychological benefits of plant-based diets. Researchers noted that gut bacteria play a role in producing neurotransmitters like serotonin, which influence mood and cognitive function. Plant-based diets rich in prebiotic fibers may enhance these microbial functions, potentially reducing stress and improving mental health.
“The quantity and diversity of plant-based foods have a very positive impact on the microbiome,” stated Nicola Segata, lead researcher and head of the Computational Metagenomics Laboratory at the Cibio Department. He emphasized that simply avoiding meat or dairy isn’t sufficient without incorporating diverse, high-quality plant foods. “What we can generally recommend is eating a variety of plant-based foods, particularly those rich in fiber. Food diversity is crucial,” Segata added.
The study also explored how gut microbes could serve as biomarkers for personalized dietary interventions. For example, certain microbes associated with omnivorous diets negatively impacted cardiometabolic health. Conversely, microbial profiles enriched by plant-based diets correlated with improved health markers.
This research forms part of a broader initiative in precision nutrition, aiming to tailor dietary recommendations based on individual microbiome compositions.
Researchers also highlighted the role of sustainable agriculture in promoting both human and environmental health. By increasing access to fresh, affordable plant-based foods, global dietary patterns could shift to support healthier microbiomes. This aligns with global sustainability goals, as reducing reliance on animal-based foods can significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions and preserve natural ecosystems.
As dietary preferences evolve, understanding their biological and ecological impacts becomes increasingly vital. This study demonstrates that embracing plant-based diets benefits both individual health and the planet. However, achieving these benefits depends on the quality and diversity of the foods consumed. Whether omnivore, vegetarian, or vegan, prioritizing whole, fiber-rich foods can significantly enhance gut health and overall well-being.
The research underscores the interconnectedness of diet, health, and environment, offering actionable insights for individuals and policymakers alike. By aligning dietary choices with microbiome science, it’s possible to achieve healthier outcomes for people and the planet.
The findings also emphasize the need for education and outreach to ensure that individuals understand how their dietary choices impact their microbiomes and the broader ecosystem.
Moving forward, this research paves the way for advancements in precision nutrition. By leveraging data from large-scale studies, healthcare providers could develop personalized dietary plans to optimize gut health and mitigate disease risks. This approach could revolutionize public health strategies, making them more effective and sustainable.

















