Baseline characteristics of the participants
Table 1 depicts the participant characteristics. Out of 438,681 participants, 75,056 (17.11%) had CMDs. Among them, 15.12% had one CMDs, 1.90% had two CMDs, and 0.09% had three CMDs. Individuals with one, two, or three CMDs were compared to those without CMDs. The former group was older, had more males and retirees, lower education levels, poorer economic status, lower normal BMI rates, fewer carriers of the APOE ε4 gene, more dyslipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia, and higher usage of lipid-lowering drugs and aspirin. Furthermore, this group has a high proportion of patients with moderate and severe serum 25(OH)D deficiency and hypertension, and a relatively low proportion of patients with depression. Significant statistical differences in exposure to ambient air pollutants and healthy lifestyle scores were found between people with and without CMDs, with a higher proportion of people with CMDs being exposed to medium and high levels of ambient air pollutants compared to those without CMDs. Healthy lifestyle scores of 0–1, 2–3, and 4 were higher in individuals with CMDs compared to those without CMDs, whereas the proportion of scores of 5–7 was lower in those with CMDs.
The risk of developing mild cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia in patients with CMDs was 1.951, 1.554, 1.216, and 2.032 times higher than in those without CMDs, respectively [mild cognitive impairment: HR = 1.951, 95% CI: 1.404, 2.710; all-cause dementia: HR = 1.554, 95% CI: 1.473, 1.640; Alzheimer’s disease: HR = 1.216, 95% CI: 1.204, 1.228; vascular dementia: HR = 2.032, 95% CI: 1.799, 2.296]. The risk of developing mild cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia in the population seems to increase with the increase in the number of CMDs. Patients with all three types of CMDs have the highest risk of total dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia (Table 2). Furthermore, the rates of mild cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia per 1,000 person-years were 0.038 (95% CI: 0.03, 0.04), 0.943 (95% CI: 0.92, 0.97), 0.455 (95% CI: 0.44, 0.47) and 0.155 (95% CI: 0.14, 0.17), respectively, for those without CMDs. The prevalence rates of mild cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia per 1000 person-years in the CMDs population were 0.064 (95% CI: 0.05, 0.08), 2.593 (95% CI: 2.50, 2.69) and 1.010 (95% CI: 0.95, 1.010), respectively (Table 3).
Effect of ambient air pollution on mild cognitive impairment and dementia risk in individuals with cardiometabolic diseases
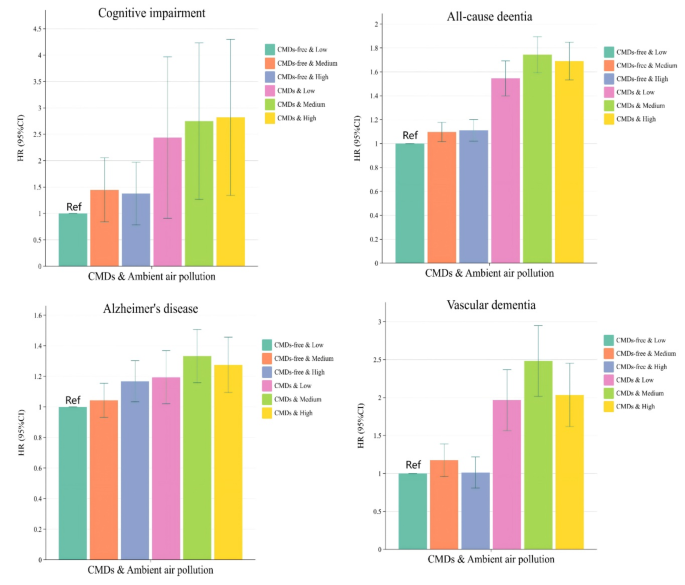
When analyzed in combination with CMDs status and ambient air pollution factors, patients with non-CMDs and those with CMDs showed consistent associations with a higher risk of mild cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia if they maintained high levels of ambient air pollution exposure (Fig. 1). The risk of mild cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia is 2.562 times, 1.686 times, 1.267 times, and 2.006 times higher, respectively, in patients with CMDs and high exposure to ambient air pollution than in patients without CMDs and low exposure to ambient air pollution (Table 4). Among them, high levels of exposure to PM2.5, PM2.5−10, PM10, NO2, and NOX may elevate the risk of different dementia subtypes in patients with CMDs (Tables S7). The incidence rates of mild cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia per 1000 person-years in individuals with CMDs exposed to high levels of ambient air pollution were 0.087 (95% CI: 0.06, 0.12), 2.699 (95% CI: 2.54, 2.86), 1.050 (95% CI: 0.95, 1.15), and 0.743 (95% CI: 0.66, 0.83), respectively (Tables S8).
Association between exposure to ambient air pollution and risk of developing mild cognitive impairment and several dementia subtypes in patients with cardiometabolic disease. Abbreviations: CMDs, Cardiometabolic disease; HR, hazard ratios; CI, Confidence Intervals;In the model, we controlled for basic sociodemographic factors [age, sex, race, educational level, occupational status, TDI, BMI] and health-related concerns [APOE genotype; history of hypertension; history of depression; dyslipidemia; hypertriglyceridemia; aspirin use; lipid-lowering medication use; serum 25(OH)D levels].
In the stratified study using the presence of CMDs, high levels of ambient air pollution increased the risk of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in the non-CMDs population by 12.0% and 25.3%, respectively [all-cause dementia: HR = 1.120, 95% CI:1.030,1.218; Alzheimer’s disease: HR = 1.253, 95% CI:1.123,1.398] (Table 5). Compared with the lowest quartile of PM2.5 exposure, the risk of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in non-CMDs individuals exposed to the highest quartile of PM2.5 is 1.137 and 1.242 times higher, respectively (Tables S9). High ambient air pollution exposure increased the risk of developing vascular dementia in patients with CMDs by 1.086 times compared to low exposure (Table 5). In addition, ambient air pollution was not found to be associated with the risk of developing mild cognitive impairment (P > 0.05) (Table 5 and Tables S9).
Effect of healthy lifestyle score on mild cognitive impairment and dementia risk in individuals with cardiometabolic diseases
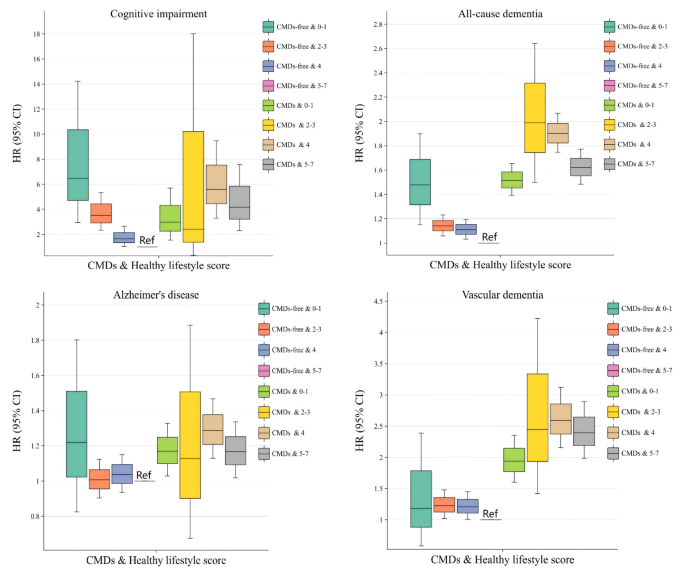
When analyzed in combination with CMDs status and healthy lifestyle score factors, if patients with non-CMDs and those with CMDs maintained high healthy lifestyle scores, their risk of all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia is lower (Fig. 2). The risk of mild cognitive impairment and different dementia types decreased as healthy lifestyle scores increased in individuals with or without CMDs. Those with scores of 5 to 7 and no CMDs had the lowest risk for mild cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, and vascular dementia. The risk of developing mild cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia was 2.973-fold, 1.516-fold, 1.169-fold, and 1.940-fold higher, respectively, among those with CMDs and a healthy lifestyle score of 0 to 1 than among those without CMDs and a healthy lifestyle score of 5 to 7 (Table 6). The incidence rates per 1000 person-years for mild cognitive impairment, all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia in patients with CMDs in the Healthy Lifestyle Score 0–1 subgroup were 0.095 (95% CI: 0.02, 0.39), 2.951 (95% CI: 2.28, 3.82), 0.912 (95% CI: 0.57, 1.45), and 0.814 (95% CI: 0.49, 1.33), respectively (Table S10).
Association between healthy lifestyle score and risk of developing cognitive impairment and several dementia subtypes in patients with cardiometabolic disease. Abbreviations: CMDs, Cardiometabolic disease; HR, hazard ratios; CI, Confidence Intervals;In the model, we controlled for basic sociodemographic factors [age, sex, race, educational level, occupational status, TDI, BMI] and health-related concerns [APOE genotype; history of hypertension; history of depression; dyslipidemia; hypertriglyceridemia; aspirin use; lipid-lowering medication use; serum 25(OH)D levels].
In studies using CMDs presence or absence as a stratifying factor, a significant statistical association was discovered between a healthy lifestyle and the risk of incident all-cause dementia and vascular dementia in individuals with CMDs. The risk of developing all-cause dementia and vascular dementia was 1.314 and 1.354 times higher, respectively, in patients with CMDs scoring 0 to 1 on the Healthy Lifestyle Score than that in those with CMDs scoring 5 to 7 (Table 7). In addition, except for the healthy diet model, there were significant statistical associations between the remaining six healthy lifestyles and the risk of developing mild cognitive impairment or different subtypes of dementia. In terms of the magnitude of the effect of a healthy lifestyle on the risk of developing mild cognitive impairment and dementia, adopting a healthy lifestyle may have the greatest impact on reducing the risk of mild cognitive impairment (Table S11).
Effect modification of ambient air pollution on mild cognitive impairment and dementia risk by lifestyle score in individuals with cardiometabolic diseases
In CMDs patients with high levels of exposure to ambient air pollution, the risk of all-cause dementia may also decrease as the healthy lifestyle subgroup score increases [0 to 1 score subgroup: HR = 3.049, 95% CI: 1.559, 5.965; 2 to 3 score subgroup: HR = 1.805, 95% CI: 1.534, 2.124; 4 score subgroup: HR = 1.525, 95% CI: 1.286, 1.808; 5 to 7 score subgroup: HR = 1.623, 95% CI: 1.383, 1.906] (Table 8). Similar results were noted for the environmental contaminants PM2.5, and NOX (Table S12). CMDs patients exposed to moderate air pollution have the highest risk of vascular dementia in the subgroups with healthy lifestyle scores of 2–3, 4, and 5–7. Ambient air pollutants had a more statistically significant adverse effect on the risk of vascular dementia in patients with CMDs than in the non-CMDs population. In addition, in the healthy lifestyle score 0 to 1 subgroup, no associations were found between patients with CMDs exposed to high levels of ambient air pollution and the risk of developing mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular dementia (Table 8).
When analyzing the modulatory effect of a healthy lifestyle on the impact of ambient air pollution on mild cognitive impairment and different subtypes of dementia risk in the population without CMDs and CMDs, it was found that exposure to ambient air pollution may have had a greater effect on the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in non-CMDs patients in the 5 to 7 point subgroup compared to the 2 to 3 point subgroup of healthy lifestyle scores [2 to 3 score subgroup: HR = 1.267, 95% CI: 1.025, 1.566; 5 to 7 score subgroup: HR = 1.328, 95% CI: 1.123, 1.572] (Table 9). In addition, in the healthy lifestyle score 0 to 1 subgroup, a significant statistical association was found between PM2.5 and NOX exposure and the risk of all-cause dementia in CMDs patients. In the healthy lifestyle score 2 to 3 subgroup, a significant statistical association was found between PM10 exposure and the risk of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in CMDs patients (Table S13).
At the same time, an interaction was found in this study between the scores for a healthy lifestyle and the exposure to ambient air pollution. Using low-level exposure to ambient air pollution and a healthy lifestyle score of 5 to 7 as the control group, we found that exposure to medium-level ambient air pollution and a healthy lifestyle score of 0 to 1 in non-CMDs population may have the greatest risk of mild cognitive impairment and all-cause dementia. In contrast, exposure to high levels of ambient air pollution and a healthy lifestyle score of 0 to 1 in the CMDs population may have the greatest risk of all-cause dementia and vascular dementia. These included a possible reduction in the risk of all-cause dementia and vascular dementia in patients with CMDs with increasing healthy lifestyle scores at constant levels of exposure to ambient air pollution (Table 10). Sensitivity analyses yielded similar results, further ensuring the reliability of the study (Table S14 to S25).